Managing Linux Servers will become easier when we know about cron jobs. but what are cron jobs well Cron jobs are tasks scheduled to run automatically, saving time and effort. So, Let’s learn How to Check Cron Jobs in Linux and ensure everything is running smoothly.
To check cron jobs in Linux, open the terminal and type crontab -l to see the user’s cron jobs. For system-wide jobs, check files in /etc/cron.d. To view logs, use sudo grep CRON /var/log/syslog. This helps you monitor scheduled tasks and ensure they run properly. Let’s see this in detail.
What Are Cron Jobs? 🤔
Cron jobs are similar to our alarm which reminds us and perform a specific task at a particular time. They can do :
- Back up data.
- Clean up temporary files.
- Run system maintenance tasks.
Now let’s see how can we exactly check the cron jobs.
Read Also: The Secret Linux Hacks Only Pros Know.
How to View Cron Jobs for a User 🧑💻
To check Cron Jobs for a specific user run the below command in your terminal:
crontab -lIt will show Cron Jobs for the current user 🛠️. Example output:
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/backup.sh It means a backup script runs daily at 2 AM.
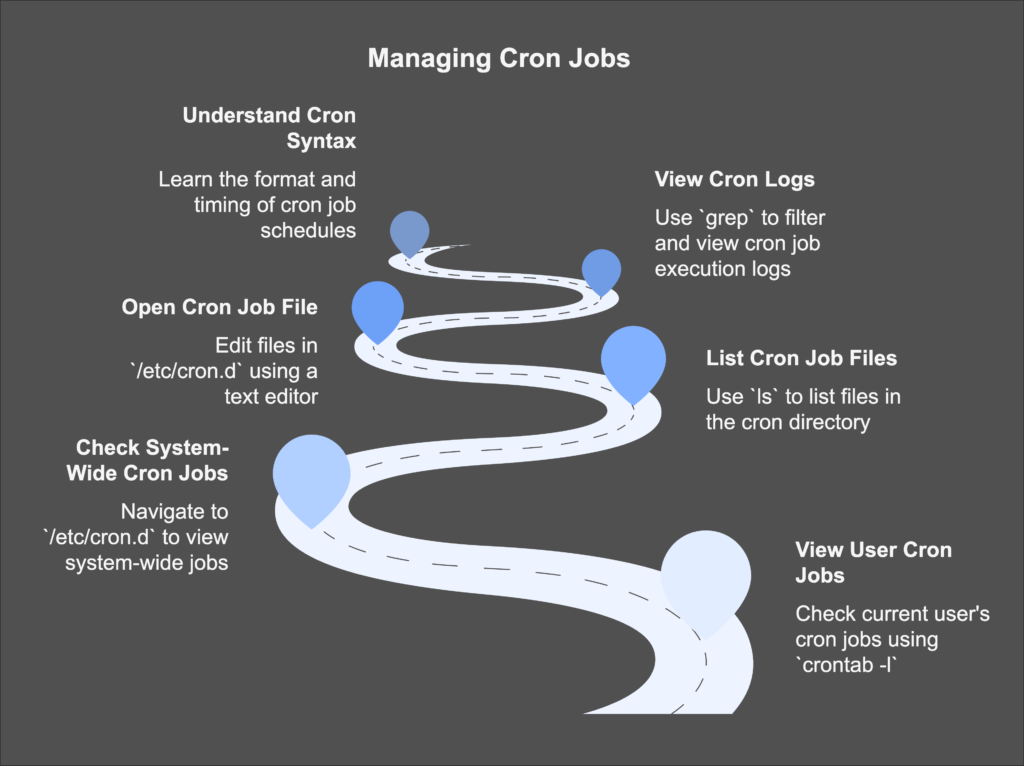
How to Check System-Wide Cron Jobs 🌐
Sometimes we need to check the System-wide Cron Jobs because it is set to the whole system, not for a single user. To check System-wide Cron Jobs follow the below steps and commands:
- first, go to the Sytemt-wide cron directory by running the below command
cd /etc/cron.d Now list the files using the ls command in Linux:
lsNow after listing the files, every file may contain the Cron jobs set by the system or other users. You can easily check by opening the file in the text editor by running the below command:
nano /etc/cron.d/filename You will see the scheduled Cron jobs make sure to replace the filename with your own filename.
How to Check Cron Logs 📝
To see when cron jobs have been executed, we can easily understand by checking the logs by running the below command:
sudo grep CRON /var/log/syslogThis command will display all Cron-related activities and check the timestamps to confirm the execution.
Pro Tip: Use grep to filter logs for specific jobs or errors!
How to Understand Cron Job Syntax 📅
Cron jobs follow a specific syntax like the below one:
* * * * * /path/to/commandEach * represents:
- Minute (0–59)
- Hour (0–23)
- Day of the month (1–31)
- Month (1–12)
- Day of the week (0–7)
💡 Example:
30 6 * * 1 /path/to/script.shby seeing this out we can easily say that This job runs every Monday at 6:30 AM.
Final Tips to Manage Cron Jobs Like a Pro 🏆
- Double-check schedules: Use crontab -l regularly to confirm.
- Backup your crontab: Run crontab -l > backup.txt to save it.
- Test your scripts: Ensure they work before adding them to cron.
Wrapping Up 🎉
Now we have covered all topics from checking to understanding the Cron jobs and after reading the post we can easily manage our Linux system like a PRO. Facing any issues or Do you have questions or tips? Drop them in the comments below. Thanks For reading my post 💖.







